Madeline Sponsler, FISM News
[elfsight_social_share_buttons id=”1″]
Fears of famine in Yemen are resurfacing, the United Nations says. A U.N. report Wednesday said Yemen was returning to “alarming” levels of food insecurity.
“My son is sick and I don’t know where to take him. He has fever and I’ve nothing to treat him, I can’t even get water,” said Zaina Muhammad, mother to Hassan and his six siblings. “Sometimes we go days without washing.”
Coronavirus restrictions, reduced remittances, locusts, floods and significant underfunding of this year’s aid response have compounded an already dire hunger situation after five years of war.
Resurgent violence in recent weeks between warring parties, despite U.N. peace efforts, is also killing and injuring civilians.
Famine has never been officially declared in Yemen. U.N. warnings in late 2018 of impending famine prompted an aid ramp-up after which the World Food Programme fed up to 13 million a month.
“Now all those improvements are at risk,” WFP spokesperson Elisabeth Byrs said.
Despite mounting economic and health pressures on Yemen, the world’s largest aid response is scaling back due to insufficient funding.
Nutrition services for 2.5 million children could cease by the end of August. The WFP already in April halved food aid to alternate months in north Yemen.
“They are on the brink of famine but it is not famine yet… It’s not too late,” she said, appealing to donors.
Displaced five times by war, Hassan’s family now live in rural Hajjah, one of the poorest regions, with no income.
“Warplanes circle above us, Houthi armaments are nearby; we cannot move on,” Zaina said.
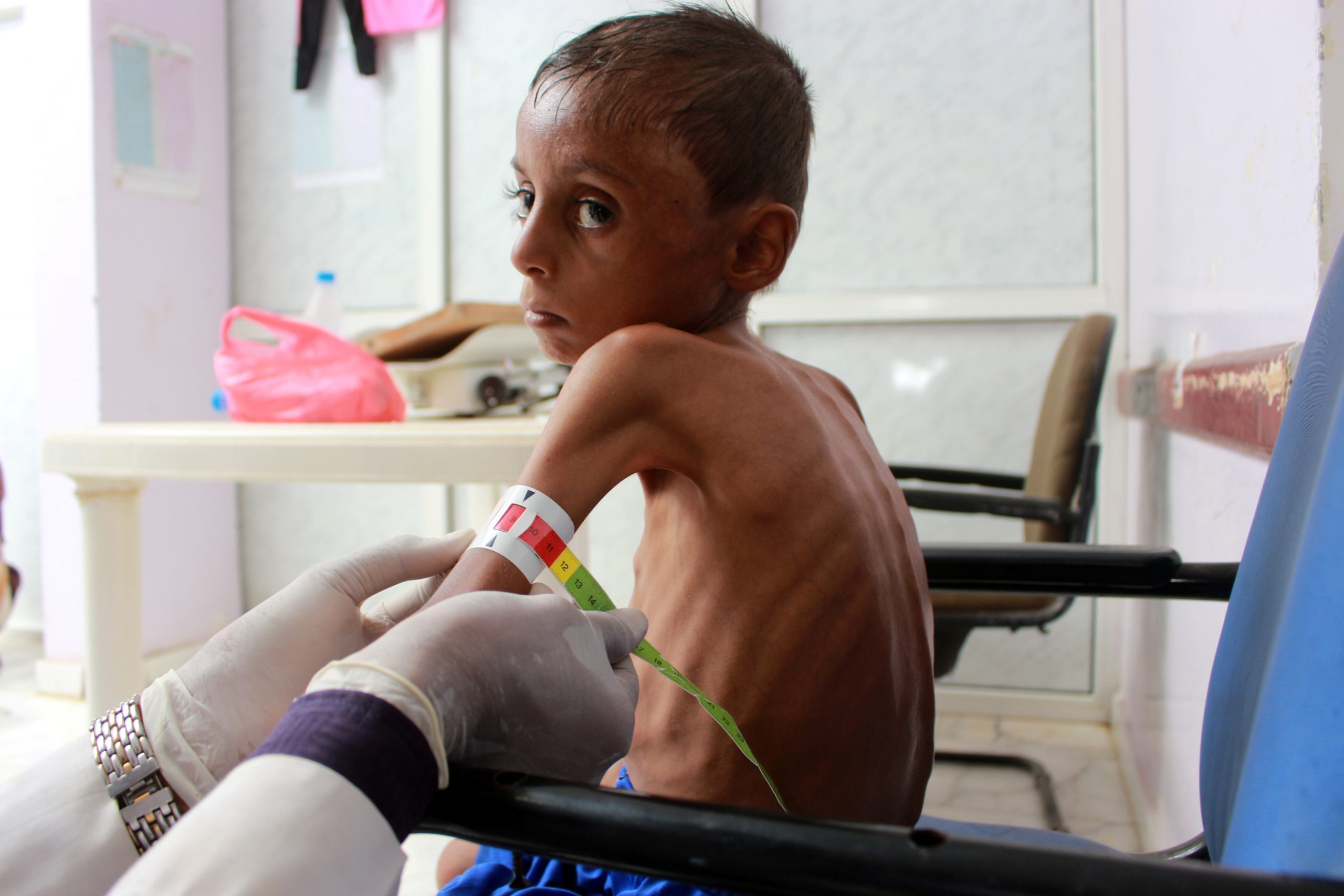
Nurse Makieh al-Aslami watched Hassan’s father carry the boy, unable to walk or react, into the malnutrition clinic she runs.
“Hassan has no health problems. His problem is hunger,” she said. “Like all children, Hassan needs play, school… It’s like he’s in a cage, with hunger increasing depression.”
The number of malnourished under-fives could rise by 20% to 2.4 million by year-end on funding shortfalls, UNICEF has said.
A Saudi-led coalition intervened in Yemen in March 2015 to restore the Yemeni government ousted from power in the capital Sanaa by the Iran-aligned Houthis. 80% of the population relies on humanitarian aid.
According to the U.N.’s Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) analysis, 40 percent of south Yemen will face high levels of acute food insecurity in July-December, up from 25 percent in February-April.
IPC data for north Yemen, where most Yemenis live and which is controlled by Houthi authorities, is due in September.
“If we wait for famine to be declared, it will already be too late as people will already be dying,” Byrs said earlier this month.
